-
Home
-
About Us
-
Products
-
Total Solution
-
News
-
Blog
-
Contact Us
Leave Your Message
-
-
Phone
-
E-mail
-
Whatsapp
-
Whatsapp



When it comes to powering your devices on-the-go or providing backup power for your home, selecting the right voltage inverter is crucial. A voltage inverter is a device that converts direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC), enabling you to use household appliances and electronics away from traditional power sources. With various options available on the market, understanding how to select the appropriate voltage inverter for your specific power needs is essential for ensuring efficiency and functionality.
As you delve into the process of choosing a voltage inverter, you'll want to consider several key factors, including the wattage requirements of your devices, the type of inverter required for your application, and the overall efficiency of the unit. Different situations call for different kinds of inverters, ranging from pure sine wave inverters ideal for sensitive electronics to modified sine wave inverters suited for more robust appliances. By assessing your power requirements and the nature of the devices you'll be using, you can make an informed decision that perfectly aligns with your energy needs.

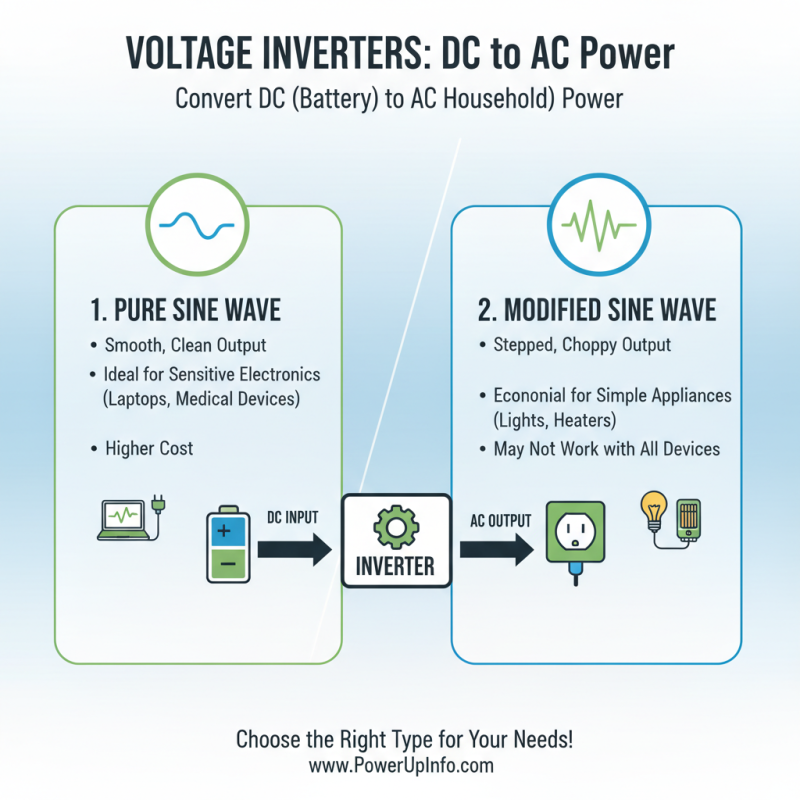
Voltage inverters are essential devices that convert direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC), enabling the use of various electrical appliances that require AC power. Understanding the basics of voltage inverters helps you make informed decisions when selecting the right one for your needs. Inverters come in two main types: pure sine wave and modified sine wave. Pure sine wave inverters produce a smooth and consistent output, making them ideal for sensitive electronics, while modified sine wave inverters are often more economical but may not be compatible with all devices.
When choosing a voltage inverter, consider your power requirements and the total wattage of the devices you'll be using. It's crucial to assess both the starting wattage, which is higher for devices with motors, and the running wattage. This will help you ensure that the inverter can handle your devices' power demands effectively.
**Tips:** First, always opt for an inverter that has a slightly higher wattage rating than you currently need to accommodate future power needs. Second, pay attention to the inverter's efficiency rating; higher efficiency means less energy loss during conversion. Finally, think about the inverter's portability if you require a mobile power solution—lighter models can be easier to transport. By keeping these basics in mind, you can confidently choose the right voltage inverter to suit your power needs.
Identifying your power needs and requirements is a crucial first step in selecting the right voltage inverter. Start by determining which devices and appliances you intend to power. Calculate the total wattage needed by adding the wattage of each device. It's essential to consider not only the continuous wattage but also the starting wattage, especially for appliances with motors, which may require more power momentarily when starting up. Understanding these figures will help you choose an inverter that can handle the demands of your equipment without overloading.
Next, assess the voltage requirements of your devices. Most household appliances operate on either 12V or 24V DC, while many larger devices may operate on 120V or 240V AC. Make sure the inverter you select converts the appropriate voltage type. Additionally, consider the duration for which you will require power. If you plan to use the inverter for extended periods, opt for a model that can sustain your power needs without overheating or depleting your battery quickly. By carefully evaluating these factors, you can ensure that the inverter you choose aligns perfectly with your power requirements.
When selecting a voltage inverter, understanding the different types available can help you make an informed decision tailored to your power needs. The two primary categories of voltage inverters are modified sine wave inverters and pure sine wave inverters. Modified sine wave inverters convert direct current into an approximation of alternating current. They are typically more affordable and effective for basic applications, such as powering simple household appliances or lighting. However, these inverters may not provide a consistent performance with more sensitive electronics, potentially causing noise issues or erratic behavior.
On the other hand, pure sine wave inverters produce a smooth, consistent waveform similar to that found in standard electrical outlets. This makes them ideal for operating sensitive electronic devices, such as medical equipment, computers, and high-end audio systems. While they are generally more expensive than their modified counterparts, the enhanced reliability and efficiency can justify the investment for those who rely on precision and performance. Ultimately, considering the type of devices you intend to power and the specific requirements of your applications is crucial in selecting the right voltage inverter to meet your power needs effectively.
| Inverter Type | Output Waveform | Efficiency (%) | Typical Applications | Price Range ($) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Modified Sine Wave Inverter | Modified Sine Wave | 85-90 | Basic appliances, lights | 100 - 300 |
| Pure Sine Wave Inverter | Pure Sine Wave | 90-95 | Sensitive electronics, solar systems | 300 - 800 |
| Grid-Tie Inverter | Variable | 95-98 | Solar energy systems | 500 - 1500 |
| Off-Grid Inverter | Pure Sine Wave | 90-95 | Remote power systems | 400 - 1200 |
When selecting the right voltage inverter, assessing its capacity and efficiency is crucial for meeting your power needs effectively. Inverter capacity is typically measured in w watts, indicating the maximum power it can deliver. To choose the right capacity, you should first calculate the total wattage of the devices you plan to power. This involves adding up the watt ratings of each appliance and accounting for any potential surges at startup, which can be significantly higher than the running wattage. It's essential to select an inverter with a capacity exceeding your total wattage to ensure seamless operation and prevent overload.
Efficiency, on the other hand, refers to how effectively the inverter converts DC power from batteries into AC power for your devices. An inverter’s efficiency rating, usually expressed as a percentage, indicates how much of the input power is converted into output power. A higher efficiency rating means less energy loss during conversion, which is particularly important for battery-operated systems. When choosing an inverter, look for models that offer high efficiency while meeting your power requirements, as this will not only save energy but also extend the life of your power source.
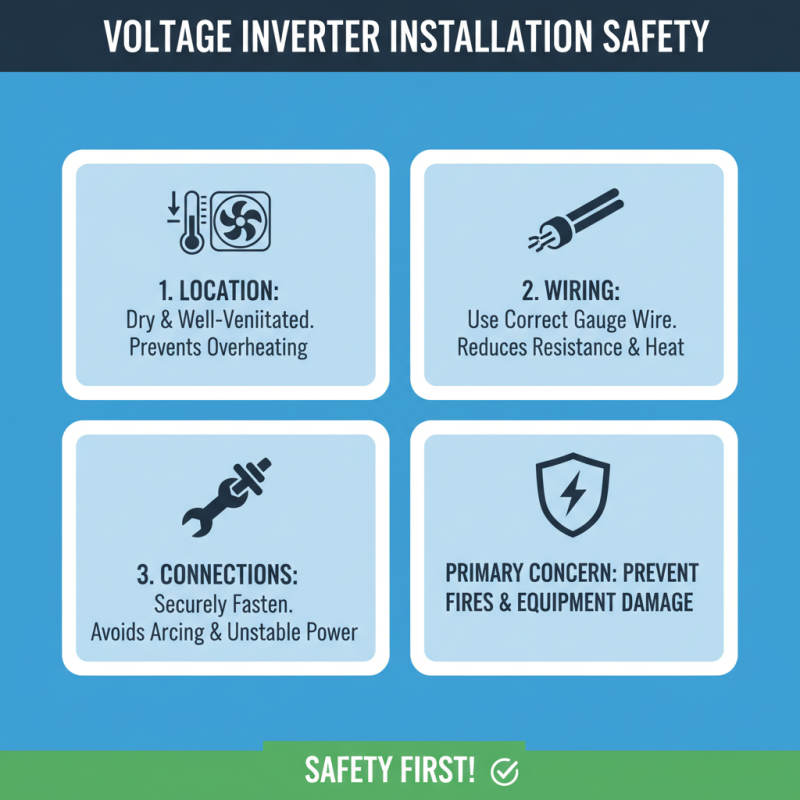
When installing a voltage inverter, safety should be the primary concern. Proper installation techniques are crucial to prevent potential hazards such as electrical fires or equipment damage. First, ensure that the inverter is installed in a dry, well-ventilated area to avoid overheating. Selecting appropriate wiring is essential; using the correct gauge wire minimizes resistance and energy loss, while reducing the risk of overheating. Additionally, make sure to secure connections tightly to prevent arcing and ensure a stable power supply.
Another important consideration is grounding the inverter properly. A good grounding system not only protects the inverter from electrical surges but also ensures user safety. Follow all manufacturer recommendations for grounding, which often involve connecting the inverter's ground terminal to a grounding rod or pipe. It's also advisable to utilize circuit breakers or fuses in the installation to provide an extra layer of protection against overloads. By adhering to these installation and safety guidelines, users can maximize the efficiency of their voltage inverter while ensuring a secure operating environment.