-
Home
-
About Us
-
Products
-
Total Solution
-
News
-
Blog
-
Contact Us
Leave Your Message
-
-
Phone
-
E-mail
-
Whatsapp
-
Whatsapp



Choosing the right voltage inverter can be daunting. Experts emphasize understanding your needs. John Smith, an industry expert, once stated, "Choosing a voltage inverter is about matching power with purpose."
Voltage inverters convert direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC). This switch is crucial for powering devices efficiently. Knowing how much power you need is the starting point. Overestimating can lead to wasted energy, while underestimating may leave you frustrated.
Consider the type of appliances you'll power. Some devices require pure sine wave inverters for smooth operation. Others can work with modified sine wave inverters. This distinction is often overlooked. Reflect on your specific needs before making a decision. A thoughtful choice can enhance performance and save costs.
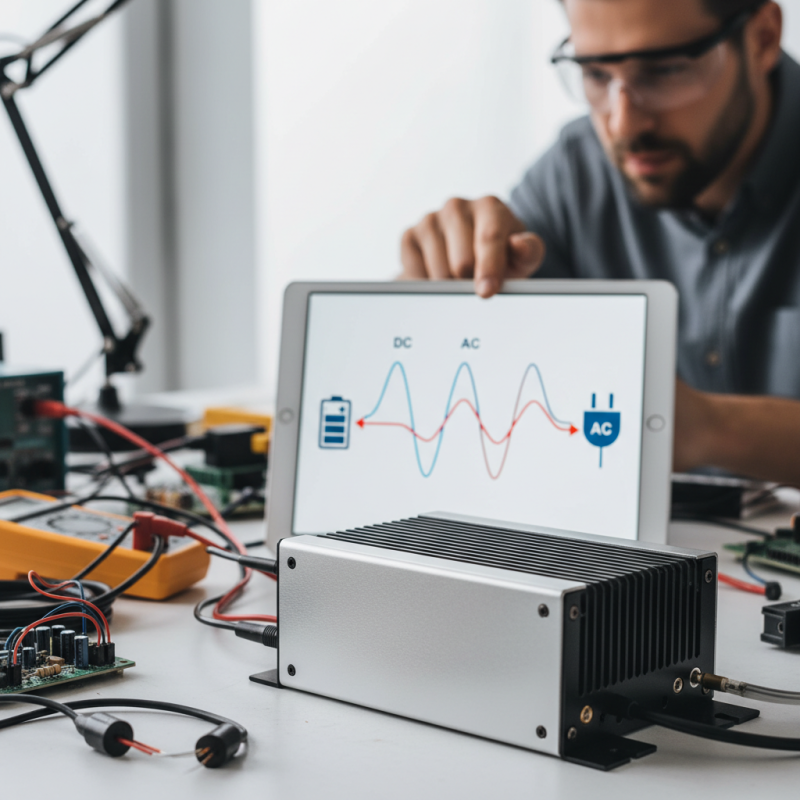

Voltage inverters play a crucial role in converting DC power to AC power. This transformation is essential for operating many household appliances. They come in various specifications that cater to different needs. Understanding these specifications is vital before making a purchase.
When choosing a voltage inverter, consider your power requirements. How many devices do you plan to run? Each device has a specific wattage. Make sure to calculate the total wattage needed. This will help you avoid overloading the inverter.
The type of inverter is also important. There are pure sine wave and modified sine wave inverters. Pure sine wave models mimic grid power closely, providing smooth operation. Modified sine wave versions are simpler and cheaper, but they may not suit all devices. They can cause inefficiencies in some electronics.
It’s crucial to evaluate what your devices require, considering potential risks. Make a list of your electronics and their power needs. Reflect on how often you’ll use the inverter. This will inform a more thoughtful purchase decision.
Choosing the right voltage inverter can be tricky. Several key factors need consideration. First, assess the power requirements of your devices. Each device has a specific wattage. Calculating total wattage will help in selecting an appropriate inverter capacity. If you underestimate this, your devices may not function properly.
Next, consider the type of inverter. Modified sine wave inverters are often cheaper but may not work well with sensitive electronics. Pure sine wave inverters provide a cleaner output, essential for intricate devices. However, they are typically more expensive. Know your device's tolerance; some might handle distorted power better than others.
Don't forget about mobility. If you need a portable solution, choose a lightweight inverter. Check the durability as well. An inverter should withstand various environments, especially if used outdoors. Additionally, think about ventilation. Overheating can cause a malfunction. It's important to ensure there's adequate airflow around the unit, especially in small spaces. Careful selection can avoid disappointment down the road.
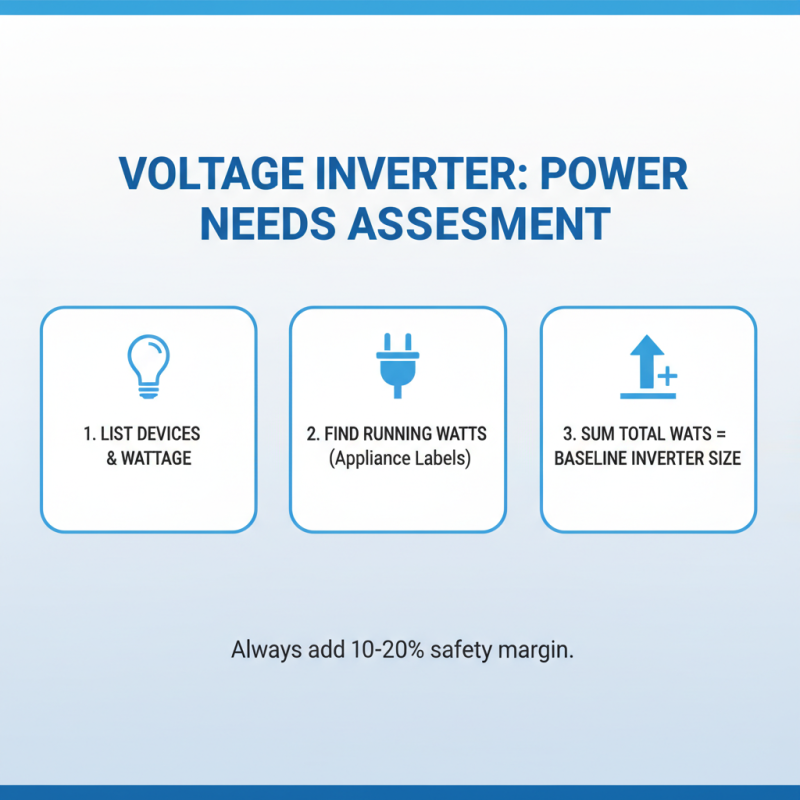
Assessing your power needs is crucial when selecting a voltage inverter. Start by calculating the wattage of all devices you intend to power. Look at the labels on your appliances. Sum the running wattage ratings. This will give you a baseline for your inverter’s requirements.
Surge capacity is another important factor. Many devices, like power tools, need extra power to start. This surge is often several times the running wattage. It’s a common oversight. You might think a lower-rated inverter is enough. However, if it can't handle the surge, it can fail.
Consider future needs as well. You may acquire more devices later. Always account for growth. A little extra capacity will save you hassle down the line. Keep these numbers in mind as you explore options. It’s an essential part of ensuring your setup works efficiently.
When choosing a voltage inverter, understanding the types is crucial. Two main types exist: pure sine wave and modified sine wave. A pure sine wave inverter produces a smooth, clean output. This type is ideal for sensitive electronics. It mimics the power supplied by the grid. Therefore, devices like computers and medical equipment run efficiently with it.
On the other hand, modified sine wave inverters are more affordable and simpler. They produce a choppy waveform. While many devices can function correctly with this type, issues may arise. Some appliances might not run as smoothly. Motors can overheat or create noise. Evaluating the specific needs of your devices is essential. Consider what you are powering.
If cost is a significant factor, you may lean towards modified sine wave. However, think about the long-term effects. Even a small disturbance in electrical flow can lead to failures. Choosing the right inverter is more than just price. It's about ensuring reliable performance for your needs.
When selecting a voltage inverter, efficiency ratings play a pivotal role. These ratings indicate how much energy is converted into usable power. A higher efficiency means less energy waste. For instance, a model with an 85% efficiency uses only 85 units of energy to produce the same output, while 15 units are lost. This can significantly impact operating costs over time.
Recent studies show that an efficient inverter can reduce energy bills by up to 30%. Many consumers overlook this factor. They may focus solely on initial costs. However, low-efficiency units lead to higher long-term expenditures. A few percentage points in efficiency can translate into substantial savings.
Choosing an inverter involves understanding its operational demands. Underestimating power needs can lead to performance issues. If the inverter is not up to the task, it might overheat or fail. Regular evaluations of efficiency ratings should be a priority. The right inverter not only meets immediate power requirements but also adapts to future needs. Be wary. Efficiency isn't merely a number; it directly correlates to performance and reliability over time.