
-
Home
-
About Us
-
Products
-
Total Solution
-
News
-
Blog
-
Contact Us
Leave Your Message
-
-
Phone
-
E-mail
-
Whatsapp
-
Whatsapp



When it comes to powering various electronic devices and equipment, choosing the right electric inverter is crucial for efficiency, safety, and overall performance. An electric inverter serves as a vital link in converting direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC), making it essential for both recreational and residential applications. With a multitude of options available on the market, selecting an inverter tailored to your specific needs can seem daunting. However, understanding the key factors and considerations involved can significantly simplify the decision-making process.
In this article, we will explore ten essential tips to guide you in selecting the perfect electric inverter that aligns with your power requirements and budget constraints. Whether you need an inverter for camping, backup power, or for running home appliances, these tips will help you navigate the complex landscape of inverter technology. From understanding wattage requirements to evaluating portability and additional features, this guide aims to equip you with the knowledge needed to make an informed choice for your electrical power needs.

When choosing the right electric inverter, understanding the types available based on application is crucial. Inverters can be broadly categorized into three main types: modified sine wave, pure sine wave, and grid-tie inverters. Modified sine wave inverters are generally more affordable and suitable for small appliances. However, for sensitive electronics or devices requiring a stable power supply, pure sine wave inverters are recommended due to their cleaner output. A report by the International Energy Agency (IEA) indicates an increasing preference for pure sine wave inverters in residential setups, reflecting the demand for higher efficiency and reliability.
When selecting an inverter, consider your energy needs and usage patterns. For instance, if you plan to run multiple high-demand appliances, a higher-capacity inverter may be necessary. Additionally, assessing your power source is critical; grid-tie inverters are ideal for those who intend to connect their systems to the electrical grid, potentially reducing energy costs through net metering. As the market evolves, a survey from the Energy Storage Association reports that nearly 70% of homeowners prioritize inverter efficiency and reliability as key factors in their purchasing decisions.
Remember to evaluate inverter features such as overload capability and safety mechanisms. Incorporating these considerations can help ensure your inverter meets both current and future energy needs. As data from the Renewable Energy World suggests, investing in a quality inverter can significantly enhance energy savings and performance, making it a worthy investment for both residential and commercial applications.
| Application | Type of Inverter | Power Output (W) | Efficiency (%) | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Residential | Pure Sine Wave Inverter | 3000 | 90 | Running appliances smoothly |
| Automotive | Modified Sine Wave Inverter | 1500 | 85 | Powering small devices |
| Off-Grid | Grid-Tie Inverter | 5000 | 95 | Solar panel integration |
| Industrial | High-Power Inverter | 10000 | 92 | Heavy machinery operation |
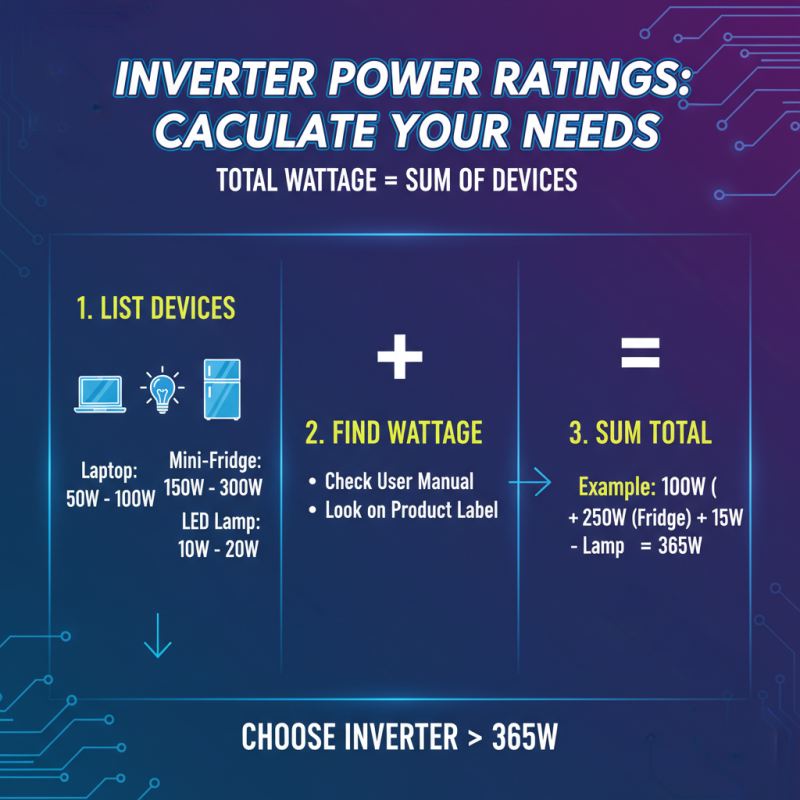
When selecting the right electric inverter for your needs, one of the most critical steps is evaluating power ratings by calculating your wattage requirements. To begin, list all the devices you intend to power with the inverter. Each device will have a wattage rating, usually found in the user manual or on the product itself. So, if you plan to run a combination of devices, sum up their wattages to determine your total requirement.
An essential tip is to include a buffer in your calculations. Often, devices require a surge of power when they start up, which can be significantly higher than their running wattage. A good practice is to add an additional 20-30% to your total wattage needs. This extra capacity ensures that your inverter can handle peak demands without overload, maintaining the reliability of your power supply.
Additionally, consider the inverter type based on your application. Pure sine wave inverters are ideal for sensitive electronics, while modified sine wave inverters could suffice for less complex devices. By carefully assessing your wattage needs and understanding the types of inverters available, you will be well-equipped to choose the right electric inverter tailored to your requirements.
When selecting an electric inverter, understanding efficiency ratings is crucial for optimizing performance and energy consumption. Efficiency refers to how much of the input energy is converted to usable output energy, typically expressed as a percentage. According to a report by the U.S. Department of Energy, inverters can have efficiency ratings ranging from 80% to over 95%. An inverter with a higher efficiency rating minimizes energy loss during conversion, which is particularly vital for applications with high energy demands, such as solar power systems and battery storage.
Moreover, the importance of inverter efficiency becomes evident when calculating the cost-effectiveness of your energy solutions. For instance, a 10% increase in inverter efficiency could lead to substantial savings over time, especially in larger installations. The National Renewable Energy Laboratory estimates that, for a solar photovoltaic system, even a slight improvement in inverter efficiency can translate to an additional 200-300 kWh of electricity produced annually, depending on system size and geographic location. Therefore, investing in a high-efficiency inverter not only enhances system performance but can significantly reduce long-term operational costs.
When selecting the right electric inverter, understanding key features is essential to meet your specific needs. One of the most critical aspects is battery compatibility. According to a report by the Electric Power Research Institute, the efficiency of inverters can vary significantly based on the type of battery they are designed to integrate with. For instance, lithium-ion batteries offer higher energy density and longer life cycles compared to traditional lead-acid batteries, making them a preferable choice for many applications. Ensuring the inverter is compatible with high-performance batteries can yield better overall system efficiency, reducing energy losses during conversion.
Portability is another significant consideration in the selection of an electric inverter. Many industry experts recommend assessing the inverter’s weight and dimensions if you plan to use it in varied environments, such as for camping, outdoor events, or emergency situations. A survey by the International Renewable Energy Agency highlighted that portable inverters are increasingly popular, with a 20% rise in demand over the past year due to the growing trend of off-grid living. These models often feature integrated handles, lightweight designs, and compact configurations, allowing users to transport them easily while ensuring they can operate multiple devices without hassle.
When selecting the right electric inverter, understanding the balance between budgeting and performance is crucial. According to a report by the International Energy Agency (IEA), the inverter market is projected to grow significantly, driven by the increasing adoption of renewable energy solutions. A critical factor to consider is that higher performance inverters often come with a premium price. Generally, premium models can offer efficiencies exceeding 98%, while lower-end models may only reach around 90%. This efficiency translates into long-term savings on energy costs, justifying the initial investment for consumers seeking cost-effective energy solutions.
Moreover, a study by the Global Industry Analysts reveals that the cost of inverters typically ranges from $0.20 to $0.80 per watt, depending on features and performance metrics. While budget-friendly options might suffice for casual users, professionals and frequent users may find that spending a bit more upfront can lead to substantial returns in durability and energy output. Features such as smart technology integration can further enhance performance, providing insights into energy consumption and maintenance needs, which is invaluable for optimizing the overall energy efficiency of a system. Prioritizing performance in relation to cost is essential for ensuring that your selected inverter not only meets immediate energy demands but also aligns with your long-term financial goals.





